DC-DC Converters: General Information
What is a step-up DC-DC converter?
A step-up dc-dc converter is an electronic circuit that raises the DC voltage level from a lower value to a higher value. Assuming an ideal converter (100% efficiency),
Input Power = Output Power
Input Voltage — Input Current = Output voltage — Output current.
Hence a step-up dc-dc converter will reduce the input current level to a lower value at the output in the same proportion that it raises the value of the input voltage.
Step-up dc-dc converters would typically find applications in RV vehicles, heavy trucks, buses, marine vehicles, Land mobile radios, CB radios, lighting systems, AM/FM sound systems.
What is a step-down DC-DC converter?
A step-down dc-dc converter is an electronic circuit that lowers the DC voltage level from a higher value to a lower value. Assuming an ideal converter (100% efficiency),
Input Power = Output Power
Input voltage × Input current = Output voltage × Output current.
Thus, a step-down dc-dc converter will increase the input current level to a higher value at the output in the same proportion that it lowers the value of the input voltage.
Step-down dc-dc converters would typically find applications in Earth-moving equipment, heavy trucks, buses, marine vehicles, CB radios, lighting systems, AM/FM sound systems.
What is the difference between isolated and non-isolated DC-DC converters?
Isolated dc-dc converters provide full dielectric isolation (no electric contact) between input and output circuits by means of a high frequency transformer, which may be a requirement by certain safety agencies or for certain applications.
Typical applications requiring isolated dc-dc converters would be Communications, Forklifts etc.
What are the advantages of isolated DC-DC converters?
- Safety to personnel, isolation prevents input voltage from transmitting to the output in case of internal failure.
- Isolated DC-DC converters can be configured to provide positive or negative outputs from plus or minus rails.
- Voltage transients on the input are not transmitted to the output.
How can isolated DC-DC converters be configured to provide positive or negative outputs from plus or minus rails?
Isolated DC-DC voltage converters can provide positive or negative voltages from a single device. Most isolated converters have “floating” outputs that provide isolation between the case, the input and the output circuitry (See Fig.1A & B).
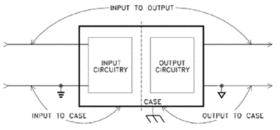
Figure 1a: Isolation between case, input and output circultry
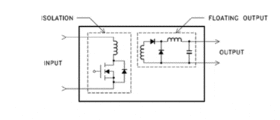
Figure 1b: Simplified input/output circultry for single output device
Connecting the output circuit reference node (ground) to the positive output will cause the output common of the device to be at a relative negative voltage. For example, by connecting the 12V output of the 12V output versions of SD or IDC series to ground, the output common may be used to supply a negative voltage (-12V) to the load. (See Fig. 2).
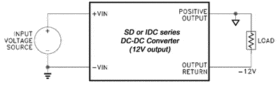
Figure 2: Isolated output configured to provide negative voltage
Isolated DC-DC converters may be also be used with either a positive or a negative input voltage source, as long as the relative polarity of the input to the device is maintained. (See Fig. 3)
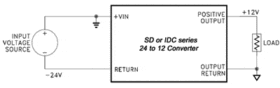
Figure 3: Negative input voltage operation
The positive input (Vin) must be positive with respect to the input return. The input return must be kept negative with respect to the Vin pin. If this polarity is reversed, the converter input will approximate a forward biased diode and permanent damage to the unit will occur. An example of operating from a negative source is shown, connecting the input return to the 24V and the input positive terminal to ground, maintaining the correct polarity. The outputs can still be made either positive or negative as described earlier.
DC-DC Converters: IDC Series fully























